Select Chapter Topics:
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
Consider a spherical conductor of radius \(r\), centred at the point \(O\). A point charge \(q(q>0)\) is placed outside the sphere, at a distance '\(d\)' from its centre \((O)\) \((d>r)\) and the sphere is earthed.

Given below are two statements:
Assertion (A):
The electric flux due to the external charge \(q\) and the induced charges on the sphere through the spherical surface \(S\) shown dotted in the diagram, is \(\left(-\dfrac{q}{\varepsilon_0}\right)\).
Reason (R):
Negative charges are induced on the surface of the conducting sphere due to the positive charge \(q\) in the vicinity, and the potential of the conducting sphere is zero.
1.
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
2.
Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
3.
(A) is True but (R) is False.
4.
(A) is False but (R) is True.
Subtopic: Capacitance |
51%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
The electric field (\(E\)) and potential (\(V\)) due to the field are related as \(E=-\dfrac{dV}{dr}\). For the \(V\) vs \(r\) graph shown, identify the correct \(E\) vs \(r\) graph:


| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Subtopic: Relation between Field & Potential |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R):
In the light of the above statements choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| Assertion (A): | Absolute potential at any point is meaningful only when some reference level for the potential is defined. |
| Reason (R): | The capacitance of any parallel plate capacitor depends on the charge on the capacitor and the voltage applied across the plates. |
In the light of the above statements choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
Subtopic: Capacitance |
64%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
As per the figure, a point charge \(+q\) is placed at the origin \(O\). Work done in taking another point charge \(-Q\) from the point \({A}(0, {a})\) to another point \(B({a},0)\) along the straight path \(AB\) is:


| 1. | \(\Big(\dfrac{-qQ}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}\dfrac{1}{a}\Big)\sqrt {2}\) |
2. | \(\Big(\dfrac{qQ}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}\dfrac{1}{a}\Big)\sqrt{2}\) |
| 3. | \(\Big(\dfrac{qQ}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}\dfrac{1}{a}\Big)\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) | 4. | zero |
Subtopic: Electric Potential Energy |
76%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
A parallel plate capacitor \((C)\) is charged by connecting it to a battery (EMF \(E\)). A dielectric slab is inserted into the space between the plates.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| (I) | The charge on the plates increases. |
| (II) | The energy stored in the capacitor increases. |
| (III) | Work is done by the battery as the slab is inserted. |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
| 1. | (I), and (II) are True. |
| 2. | (I) and (III) are True. |
| 3. | only (I) is True. |
| 4. | (I), (II), and (III) are True. |
Subtopic: Capacitance |
64%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
A dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of an isolated charged capacitor. Which of the following remains unchanged?
Choose the correct option from given ones:
| (I) | The charge on the plates. |
| (II) | The potential difference between the plates. |
| (III) | The energy stored in the capacitor. |
Choose the correct option from given ones:
| 1. | (I) only | 2. | (I) and (II) |
| 3. | (I) and (III) | 4. | (I), (II) and (III) |
Subtopic: Dielectrics in Capacitors |
72%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
The variation of potential with distance \(R\) from a fixed point is shown in the figure. The electric field at \(R=5~\text{m}\) is:
(Given, the potential, \(V\) in volts and distance, \(R\) in meters)
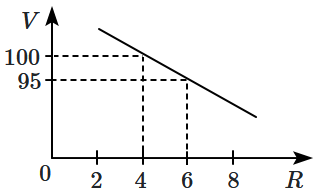
(Given, the potential, \(V\) in volts and distance, \(R\) in meters)

| 1. | \(2.5~\text{Vm}^{-1}\) | 2. | \(-2.5~\text{Vm}^{-1}\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{2}{5}~\text{Vm}^{-1}\) | 4. | \(-\dfrac{2}{5}~\text{Vm}^{-1}\) |
Subtopic: Relation between Field & Potential |
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Unlock IMPORTANT QUESTION
This question was bookmarked by 5 NEET 2025 toppers during their NEETprep journey. Get Target Batch to see this question.
✨ Perfect for quick revision & accuracy boost
Buy Target Batch
Access all premium questions instantly
The figure shows charge (\(q\)) versus voltage (\(V\)) graph for series and parallel combination of two given capacitors. The capacitances are:

1. \(50~\mu\text{F}\) and \(30~\mu\text{F}\)
2. \(20~\mu\text{F}\) and \(30~\mu\text{F}\)
3. \(60~\mu\text{F}\) and \(40~\mu\text{F}\)
4. \(40~\mu\text{F}\) and \(10~\mu\text{F}\)

1. \(50~\mu\text{F}\) and \(30~\mu\text{F}\)
2. \(20~\mu\text{F}\) and \(30~\mu\text{F}\)
3. \(60~\mu\text{F}\) and \(40~\mu\text{F}\)
4. \(40~\mu\text{F}\) and \(10~\mu\text{F}\)
Subtopic: Capacitance |
51%
Level 3: 35%-60%
Hints
Equipotential surfaces:
1. are closer in regions of large electric fields compared to regions of lower electric fields.
2. will be more crowded near the sharp edges of a conductor.
3. will always be equally spaced.
4. both (1) and (2) are correct.
Subtopic: Equipotential Surfaces |
73%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints
The potential on the surface of a spherical region varies from \(2\) V to \(4\) V from point to point. There are no charges in the interior of the region.
| Assertion (A): | The potential at the centre cannot be \(0\) V. |
| Reason (R): | Potential in the interior of a sphere must always be greater than the potential on the surface. |
| 1. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 2. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
| 3. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
Subtopic: Electric Potential |
64%
Level 2: 60%+
Hints






