A diatomic ideal gas is compressed adiabatically to of its initial volume. If the initial temperature of the gas is T, (in Kelvin) and the final temperature is a T, the value of a is
1. 8
2. 4
3. 3
4. 5
The relation between U, P and V for an ideal gas in an adiabatic process is given by relation U = a+bP V. Find the value of adiabatic exponent of this gas.
1.
2.
3.
4.
One mole of a diatomic ideal gas undergoes a cyclic process ABC as shown in figure. The process BC is adiabatic. The temperatures at A.B and C are 400 K, 800 K and 600 K respectively. Choose the correct statement:
1. The change in internal energy in whole cyclic process is 250 R
2. The change in internal energy in the process CA is 700 R
3. The change in internal energy in the process AB is -350 R
4. The change in internal energy in the process BC is -500 R
Four curves A,B, C and D are drawn in the figure for a given amount of a gas. The curves which represent adiabatic and isothermal changes are
1. C and D respectively
2. D and C respectively
3. A and B respectively
4. B and A respectively
A cube of side 5 cm made of iron and having a mass of 1500 g is heated from 25C to 400C. The specific heat for iron is 0.12 cal/g C and the coefficient of volume expansion is , the change in the internal energy of the cube is (atm pressure =
1. 320 kJ
2. 282 kJ
3. 141 kJ
4. 423 kJ
When an ideal gas is heated under constant pressure, then what percentage of given heat energy will be utilised in doing external work ?
1. 40%
2. 30%
3. 60%
4. 20%
A mass of ideal gas at pressire P is expanded isothermally to four times the original volume and then slowly compressed adiabatically to its original volume. Assuming to be 1.5 , the new pressure of the gas is
1. 2P
2. P
3. 4P
4. P/2
An engine operates by taking n moles of an ideal gas through the cycle ABCDA shown in figure. The thermal efficiency of the engine is : (Take Cv = 1.5 R, where R is gas constant)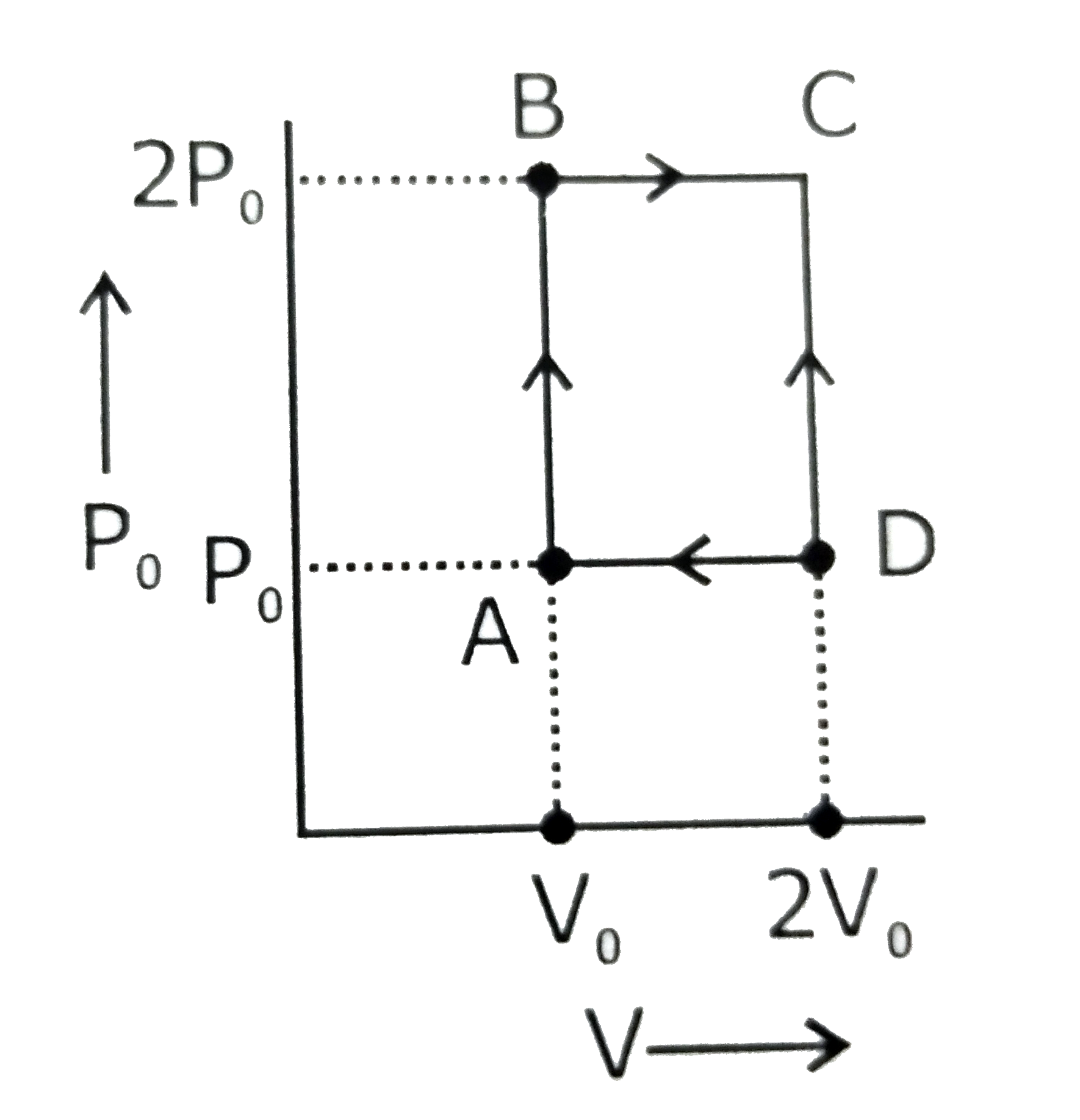
1. 0.24
2. 0.15
3. 0.32
4. 0.08
'n' moles of an ideal gas undergoes a process AB as shown in the figure. The maximum temperature of the gas during the process will be :
1.
2.
3.
4.
The equation of state for a gas is given by , where n is the number of moles and is a positive constant. The initial temperature and pressure of one mole of the gas contained in a cylinder are and respectively. The work done by the gas when its temperature doubles isobarically will be
1.
2.
3.
4.
One mole of an ideal gas at temperature T was cooled isochorically till the gas pressure fell from P to . Then, by an isobaric process, the gas was restored to the initial temperature. The net amount of heat absorbed by the gas in the process is
1. nRT
2.
3.
4.
The figure shows the P-V plot of an ideal gas taken through a cycle ABCDA. The part ABC is a semi-circle and CDA is half of an ellipse . Then
1. the process during the path is isothermal
2. heat flows out of the gas during the path
3. work done during the path is zero
4. no work done is done by the gas in the cycle ABCDA
An ideal gas is subjected to cyclic process involving four thermodynamic states, the amounts of heat (Q) and work (W) involved in each of these states
Q1 = 6000 J; Q2 = -5500 J; Q3 = -3000 J; Q4 = +3500 J
W1 = 2500 J; W2 = - 1000 J; W3 = -1200 J; W4 = J
The ratio of the net work done by the gas to the total heat absorbed by the gas is . The values of and are respectively
1. 500; 7.5 %
2. 700; 10.5 %
3. 1000, 21%
4. 1500, 15%
Two carnot engined A and B are operated in series. The engine A receives heat from the source at temperature T1 and rejects the heat to the sink at temperature T. The second engine B receives the heat at temperature T and rejects to its sink at temperature T2. For what value of T the efficiencies of the two engines are equal ?
1.
2.
3.
4.
A certain diatomic gas has the same specific heats as an ideal gas but a slightly different equation of state , . The temperature of the gas is raised from T1 = 300 K to T2 at constant pressure. It is found that work done on the has is 70% higher than what would be on an ideal gas. Choose the correct statement(s).
1. = 400 K, internal energy increases by 250 R per mole
2. = 400 K, internal energy increases by 350 R per mole
3. Total heat absorbed in the process is 450 R per mole
4. Total heat absorbed in the process is 520 R per mole
For an isothermal expansion of a perfect gas, the value of is equal to
1.
2.
3.
4.
An ideal gas goes from state A to state B via three different processes as indicated in the P-V diagram
If Q1,Q2,Q3 indicate the heat absorbed by the gas along the three processes and indicate the change in internal energy along the three processes respectively, then
1.
2.
3.
4.
A refrigerator works between 4C and 30C. It is requried to remove 600 calories of heat every second in order to keep the temperature of the refrigerated space constant. The power required is : (Take 1 cal = 4.2 joules)
1. 2.365 W
2. 23.65 W
3. 236.5 W
4. 2365 W
The specific heat capacity of a metal at low temperature (T) is given by . A 100 g vessel of this metal is to be cooled from 20 K to 4 K by a special refrigerator operating at room temperature . The amount of work required to cool in vessel is
1. equal to 0.002 kJ
2. greater than 0.148 kJ
3. between 0.148 kJ and 0.028 kJ
4. less than 0.028 kJ
Pressure p, volume V and temperature T for a certain gas are related by , where A and B are constants. The work done by the gas as its temperature changes from while pressure remains constant is
1.
2.
3.
4.
A solid body of constant heat capacity 1 is being heated by keeping it in contact with reservoirs in two ways :
(i) Sequentially keeping in contact with 2 reservoirs such that each reservoir supplied same amount of heat.
(ii) Sequentially keeping in contact with 8 reservoirs such that each reservoir supplies same amount of heat.
In both the cases body is brought from initial temperature 100C to final temperature 200C. Entropy change of the body in the two cases respectively is :
1. ln 2, 2ln 2
2. 2 ln 2, 8 ln 2
3. ln 2, 4 ln 2
4. ln 2, ln 2