Which of the following is not a characteristic of monocot stem?
| 1. | Sclerenchymatous hypodermis |
| 2. | Scattered vascular bundle |
| 3. | Open bundle |
| 4. | Endarch xylex |
Which of the following pairs of cell is relate ontogenetically?
(1) Tracheids and tracheae
(2) Sieve cell and sieve tube components
(3) Sieve tube bombers and phloem
(4) Sieve tube members and companion cell
The cork of commerce is obtained from
| 1. | Quercus | 2. | Cinchona |
| 3. | Ficus | 4. | Berberis |
Conjunctive tissue is
| 1. | parenchymatous tissue present between two vascular bundles in dicot stem |
| 2. | parenchymatous tissue present between xylem and phloem in root |
| 3. | sclerenchymatous tissue present in cortex |
| 4. | lateral meristem |
Which of the following is absent in pteridophytes?
1. tracheids
2. sieve tubes
3. xylem parenchyma
4. albuminous cells
Periderm does not include
| 1. | secondary cortex |
| 2. | secondary phloem |
| 3. | secondary xylem |
| 4. | both (2) and (3) |
In a dicot root vascular cambium develops form
| 1. | pericycle |
| 2. | pericycle and conjunctive tissue |
| 3. | endodermis |
| 4. | pericycle and pith |
Protoxylem and stomata in a dorsiventral leaf are present
| 1. | on the abaxial and adaxial sides, respectively |
| 2. | on the adaxial and abaxial sides, respectively |
| 3. | on the adaxial side |
| 4. | on the abaxial side |
Secondary phloem is near to
1. cortex
2. pith
3. secondary xylem
4. cambium
Cork cells are impervious to water due to the deposition of
| 1. | lignin |
| 2. | cutin |
| 3. | both (1) and (2) |
| 4. | none of these |
Angiosperms have
| 1. | vessels absent |
| 2. | tracheids only |
| 3. | vessels present |
| 4. | sieve tubes absent |
The meristem which occurs in grasses and regenerates parts removed by grazing herbivores is primarily
(1) Lateral meristem
(2) Intercalary meristem
(3) Rib meristem
(4) Pro meristem
Which of the following is absent in most gymnosperms?
1. Tube cells
2. Companion cells
3. Phloem fibers
4. Both 1 and 2
Which of the following is absent in mature sieve element?
| 1. | Peripheral cytoplasm |
| 2. | A large vacuole |
| 3. | Nucleus |
| 4. | All of the above. |
Which of the following is not true for companion cells?
| 1. | They are absent in monocots |
| 2. | They are parenchymatous |
| 3. | They are connected by pits to sieve tube elements |
| 4. | They maintain pressure gradient in sieve tubes. |
Which of the following is absent in monocots?
| 1. | Phloem parenchyma | 2. | Companion cells |
| 3. | Phloem fibres | 4. | All of the above. |
Which of the following do not give commercially important phloem fibers?
1. Jute
2. Cotton
3. Flax
4. Hemp
Which of the following is the main function of cuticle?
| 1. | Preventing transpiration |
| 2. | Regulating gaseous exchange |
| 3. | Storing food |
| 4. | None of the above |
When the xylem and phloem are situated at the same radius of vascular bundles, the vascular bundle is said to be
(1) Open
(2) Closed
(3) Radial
(4) Conjoint
The tangential as well as radial walls of have deposition of forming casparian strips
| 1. | Endodermis, pectin |
| 2. | Pericycle, suberin |
| 3. | Endodermis, Suberin |
| 4. | Pericycle pectin |
Which of the following is false with regard to pericycle in dicot root
| 1. | Helps to form lateral roots |
| 2. | Lies between xylem and phloem |
| 3. | Maybe multi layered |
| 4. | Helps in secondary growth. |
Tissues internal to endodermis comprise the
(1) Bark
(2) Stele
(3) Conjunctive tissue
(4) Vascular bundle
Polyarch vascular bundles are usually found in-
| 1. | Monocot roots | 2. | Dicot roots |
| 3. | Monocot stems | 4. | Dicot stems |
Match the column I with column II
Column I Column II
a. Xylem parenchyma (i) Absent in most of the monocots
b. Sclereids (ii) Long cylindrical tube-like structure
C. Phloem parenchyma (iii) Food and tannins
D. Vessel (iv) Fruit walls of nuts
1. a(i), b(ii), c(iii), d(iv)
2. a(iii). b(iv), c(i) , d(ii)
3. a(ii), b(iv), c(iii), d(i)
4. a(iii), b(ii), c(i), d(iv)
The cells shown in the below diagram are of _______ tissue and can be seen in _______ layer of the dicot stem.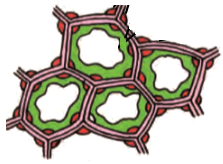
| 1. | Collenchyma, Hypodermis |
| 2. | Sclerenchyma, Sclereids |
| 3. | Parenchyma, Pericycle |
| 4. | Parenchyma, Pith |
Mechanical support to the growing parts of the plant such as young stem and petiole of leaf is provided by a living tissue called
1. Collenchyma
2. Aerenchyma
3. Chlorenchyma
4. Sclerenchyma
Which of the following is correct statement for intercalary meristems?
1. They lie at tip of roof apex
2. They lie at base of stem always
3. They are short lived and consumed during primary growth
4. They are long lived and cause increase in length
Compare diagram 'a' with 'b' and find out which statement is incorrect about difference between these two diagrams.

| 1. | In 'a' mesophyll is of two types whereas in case of 'b' mesophyll is of a single type |
| 2. | In 'a' stomata is mainly at the lower surface whereas in 'b' stomata is at both the surface |
| 3. | In 'a' vascular bundle is of different size whereas in 'b' vascular bundle is of more or less equal size |
| 4. | In 'a' xylem is towards adaxial surface whereas in 'b' xylem is towards the abaxial surface |
Apical cell theory was proposed by:
1. Nageli
2. Schmidt
3. Hanstein
4. Schupp
Quiescent centre was first discovered by:
| 1. | Clowes | 2. | Hanstein |
| 3. | Strasburger | 4. | Nageli |
Medullary rays are produced by:
1. Xylem parenchyma
2. Phloem parenchyma
3. Cambial meristem
4. None of these
Cork cells are dead because they do not possess:
| 1. | Cellulose cell wall |
| 2. | Paremeable cells wall |
| 3. | Protoplast |
| 4. | Meristematic activities |
Sclerenchyma provides:
| 1. | help in storage of materials |
| 2. | Mechanical support |
| 3. | Helps in conduction |
| 4. | Helps in assimilation |
Parenchyma differs from meristamatic cells is its
| 1. | Cell wall composition |
| 2. | Uneven thickening in cell wall |
| 3. | having cytoplasm and nucleus |
| 4. | Larger size, well developed vacuole and peripheral cytosol |
Most of the monocots are devoid of
| 1. | Phloem fibres. | 2. | Phloem parenchyma |
| 3. | Mesophyll in leaves | 4. | Sieve tubes |
lenticels present in woody trees help in
| 1. | Exchange of gases and transpiration |
| 2. | Exchange of gases and guttation |
| 3. | Only exchange of gases. |
| 4. | Elimination of exudates |
The cells of endodermis in roots
| 1. | Have intercellular spaces filled with waxy matterial called subrin. |
| 2. | Have thickenings of suberin in tangential as well as radial walls. |
| 3. | Lie inner to the pericycle. |
| 4. | Given rise to lateral roots. |
The monocot leaves have parallel veination this is reflected in
| 1. | presence of stomata in the lower epidermis. |
| 2. | Conjoint vascular bundles |
| 3. | Nearly similar sizes of vascular bundles |
| 4. | Leaves being isobilateral |
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
| 1. | Companion cell - Albuminous cells in gymnosperm |
| 2. | Companion cell - Associated with sieve cells |
| 3. | Companion cell - Nucleated structure and its nucleus controls sieve tube |
| 4. | Companion cell - Helps in maintaining the pressure gradient in sieve tube |
Semilunar patches of sclerenchyma in the dicot stem can be seen
| 1. | Above the phloem |
| 2. | In between the vascular bundles |
| 3. | In the pith |
| 4. | In between phloem and xylem |
The heartwood in trees
1. is dead but conducts water.
2. Is dead and does not conduct water.
3. Is living and gives mechanical support.
4. Surrounds the sap wood
The bulliform cells in grasses
| 1. | Are present on the upper epidermis of leaves. |
| 2. | Become turgid and cause the leaves to curl inwards under stress. |
| 3. | Are small resin filled cells. |
| 4. | Help in transpiration. |
In monocot roots the vascular bundles are
| 1. | Collateral, endarch and closed |
| 2. | Collateral, exarch and closed |
| 3. | Radial, exarch and open |
| 4. | Radial, exarch and closed |
The diagram below is transverse section of _______ and shows xylem which is _________.
| 1. | Dicot stem, Endarch. |
| 2. | Dicot stem, Exarch. |
| 3. | Monocot Root, Polyarch. |
| 4. | Dicot Root, Endarch |
Which of the following is correct with regard to monocot stem.
| 1. | Monocot stems have a well-developed collenchymatous hypodermis. |
| 2. | The vascular bundles are surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheath. |
| 3. | The cortex is differentiated into endodermis and pericycle. |
| 4. | The vascular bundles are conjoint and open. |